2023 PAR (Product & Agronomy Research) Report: Soybean Plant Populations
BY Dairyland Seed Agronomy Team
Plant population, or final stand plant population, in soybeans has been a hot topic for the last few years.
The question of what the optimum plant population for highest yield expression is will vary from field to field, as well as areas within a field, with varietal differences also impacting yields by plant population.
Diseases such as sclerotinia white mold (SWN) favor reducing plant population, and nutrient deficiencies such as iron deficiency chlorosis (IDC) favor increasing population. These factors influence the decision-making process on what is the correct plant population for a field or parts of a field. Other factors such as weed control, canopy type (bushy or narrow) and plant height will impact this decision as well.
The other aspect of looking at plant populations is that, whether it be as an agronomist or a farmer, we have all had instances in which plant populations have been reduced by some calamity such as weather (hail, wind, heat, drought, rainfall and drown outs, sandblasting or frost) or animals (deer, turkeys and deer), and we need to make decisions on if replanting is warranted.
This data will provide a better understanding as to what level the bottom for plant populations might be.
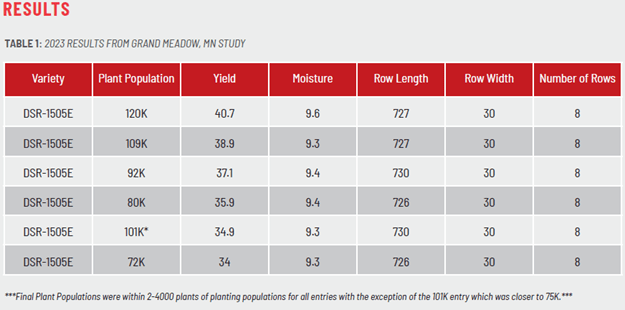
GRAND MEADOW, MINNESOTA
DSR-1505E™ were planted at various plant populations starting at 120,000 seeds per acre and ratcheting down to 72,000 seeds per acre in mostly 8-18,000 seeds per acre increments in 30-inch rows.
Final plant populations were within 2-4,000 plants of the planting population with the exception of the 101,000 entry, which ended up with a final plant population of 75,000.
This plot was planted on May 20th, 2023, which was an average to slightly later planting date for soybeans in this area, with the harvest date being October 1st, 2023.
CONCLUSION
The yields for this trial appear to be average, but were actually 3-7 bushels better than other fields in the area. This area was affected by a lack of rainfall and drought conditions all growing season, but this drought intensified in August and September, which is a critical time for soybean pod and seed development. I would attribute the 3–7-bushel yield increase versus other fields in the area to above average soil fertility and the ability of the DSR-1505E™ product, which has the potential to yield even in difficult growing conditions, especially in a variable rainfall pattern.
Typically, it has been this agronomist’s belief, that plant populations below 90- 95,000 plants per acre in this area would suggest replanting. (As we move our latitude further south as has been referenced in our studies at the Wabash Indiana PAR location in previous years this number maybe closer to 80,000 plants/acre. Conversely, as we move north, this number may increase to 100-110,000 plants/acre.) In looking at the data from this location, this year, as well as other locations from previous years, it would suggest that this belief of needing 90-95,000 plants/acre to be further reviewed and potentially changed. By reducing the planting population from 120,000 to 80,000, a 33% reduction, we decreased yield by 4.8 bushels, an 11.8% reduction. This is still a yield reduction, but not to the level as the reduction in plant population.
In previous site years, we saw a yield increase as plant populations decreased. In this site and year, we experienced the opposite, and the higher plant populations being compared were the highest yielding. We believe that is due to the extreme drought conditions we experienced in southeastern Minnesota in 2023. The increased plant population of 120,000 plants allowed more ground cover or shading for the soil. This shading of the soil resulted in cooler soils as well as allowing less wind to reach the soil level, which reduced the amount of evapotranspiration from the soil and leaf surface area.
The results, much like in previous trials, indicates that this trial needs to be replicated in different locations, with different varieties, over a longer period. Other interesting aspects to see would be replicating this trial in areas with lower fertility levels and a shorter growing season, with differing rainfall amounts. The shorter growing season, lower fertility and varying rainfall levels might suggest other outcomes over a longer period.

Brian Weller
Western Region
507.456.3034

Rod Moran
Western Region
507.456.3034

Dan Ritter
Central Region
219.863.0583

Branden Furseth
Northern Region
608.513.4265

Mark Gibson
Eastern Region
260.330.8968

Amanda Goffnett
Eastern Region
989.400.3793

Ryan Mueller
Eastern Region
989.400.3793
